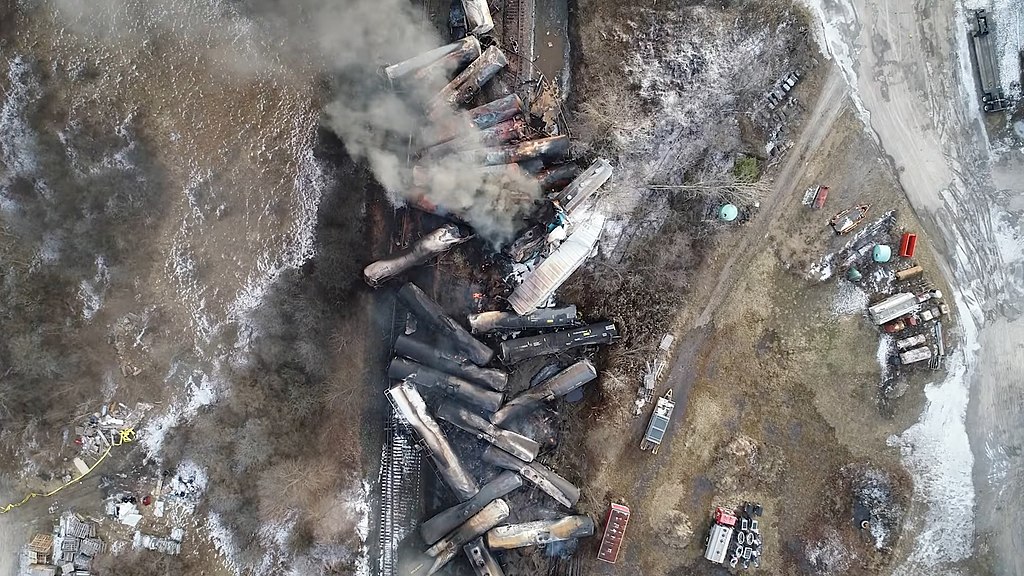
Image courtesy of National Transportation Safety Board, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
On February 3, 2023, one-third of the cars on a Norfolk Southern freight train derailed and crashed in East Palestine, Ohio1. The train was traveling from Madison, Illinois to Conway, Pennsylvania, carrying a variety of products, ranging from frozen foods to hazardous chemicals1. Of the train cars that derailed, 11 contained hazardous materials, including 5 tankers of the highly volatile chemical of vinyl chloride1,2. Vinyl chloride is an irritant to the skin, nose, and throat and an extremely toxic carcinogen that may cause liver, kidney or lung damage, and a variety of cancers1,3.
The derailment resulted in toxic chemicals being spilled into the soil, water, and air of the surrounding areas3, and massive fires sanctioned by government responders were started as a ‘controlled burning’ of the hazardous chemicals released and burned for 5 days2,3. This event was no freak accident, but rather a product of years of ignored systemic issues with railroad companies putting profits over the safety and well-being of their workers and the public4. Many union rail workers had been warning companies such as Norfolk Southern that the combination of the dramatic increase in length and tonnage of Class I carrier trains and the setbacks on maintenance and inspections would result in a major catastrophe4, such as the one that recently took place in East Palestine, Ohio.
On February 6, three days after the initial crash, residents of East Palestine were asked to evacuate the area until it was safe to return1.3. Only two days later on February 8 residents were told that the area was safe to return. However, since returning to their homes, residents have reported a lingering smell of chlorine in the air1,3. Additionally, they have reported wildlife and pets dying and experiencing symptoms, such as nausea, dizziness, headaches, watery eyes, and burning sensations of the mouth, lips, and tongue5. A spokesperson for Governor Mike DeWine told the Washington Post that doctors have not identified the chemical release as the cause of the residents’ symptoms5.
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and Pennsylvania Governor’s Office are making efforts to hold Norfolk Southern and other rail companies accountable. While speaking at a news conference in East Palestine, the head of the EPA, Michael Regan, announced that Norfolk Southern would have to find and clean contaminated soil and water supplies, make the results available online, pay back the EPA for its own cleaning efforts, and participate in public meetings at the EPA’s request6. Should the company fail to comply, the EPA will carry out the work themselves, charge Norfolk Southern for the cost of clean-up, and fine the firm up to an additional $70,000 per day6. At the same conference, Pennsylvania Governor Shapiro, joined by Ohio Governor DeWine, announced that his office referred criminal charges against the rail company and that the state prosecutor would be making the decision on whether to press charges6.
New updates regarding the ramifications of the Norfolk Southern train derailment are still coming in every day. While it is already evident that, as a result of this catastrophe, there are and will be health and environmental risks for years to come, the extent of these risks is unknown at this point. On Monday, February 23rd, crews from the EPA and Norfolk Southern continued to find and remove contaminated soils and liquids from the toxic wreck site for proper disposal7. As of Thursday, March 2nd, the process of removing and properly disposing nearly 2,000 feet of track, gravel, and soil from the derailment site has begun8. Norfolk Southern projects an April 30th completion date for rail reconstruction8. There will likely be further reports on findings regarding the accident in the coming days and weeks.
Up-to-date Timeline of the Norfolk Southern Train Derailment:
Friday, February 3: The Norfolk Southern train heading from Madison, Illinois to Conway, Pennsylvania derails near East Palestine, Ohio. Of the 150 train cars, 38 derail – 11 of which contain hazardous chemicals, mainly vinyl chloride.
Saturday, February 4: Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) arrives and begins running air pollution and water runoffs tests, detecting contaminated water in the Sulphur Run and Leslie Run streams.
Sunday, February 5: The EPA and Norfolk Southern crews continue conducting tests and recovery efforts at the contaminated water sites.
Monday, February 6: Responders conducted a controlled burn of toxic chemicals to destroy the remaining toxins. Due to the threat posed by the controlled burn, standing evacuation orders were put in place.
Wednesday, February 8: Days after the controlled burn began, Ohio Governor DeWine announced that air quality tests were coming back clean and it was safe for residents to return to their homes.
Friday, February 10 – Friday, February 17: Residents start to report symptoms. The Ohio Department of Natural Resources report that 3,500 fish were found dead in Ohio waterways as a direct result of the spill from the trail derailment. The EPA conducted air quality screenings in more than 400 homes and found levels to be safe.
Monday, February 27: Shipments of contaminated liquid and soil from the toxic derailment site to EPA-certified sites in Ohio for disposal have resumed.
Thursday, March 2: Crews begin the process of removing the tracks, gravel, and soil from the affected area and sending them away for proper disposal. With nearly 2,000 feet of rail to remove and reconstruct, the process is estimated to be completed within 2 months. Norfolk Southern’s plan sets an April 30th finish date.
References
- https://www.visualcapitalist.com/explainer-what-to-know-about-the-ohio-train-derailment/
- https://winknews.com/2023/02/20/the-lasting-environmental-impact-of-the-ohio-train-derailment/
- https://www.instagram.com/environment/?igshid=MjkzY2Y1YTY%3D
- https://twitter.com/MorePerfectUS/status/1623854130375847936
- https://www.washingtonpost.com/climate-environment/2023/02/16/ohio-train-derailment-response-toxic-contamination/
- https://www.bbc.com/news/world-us-canada-64722765
- https://www.cnn.com/2023/02/27/us/ohio-train-derailment-east-palestine-monday/index.html
- https://abcnews.go.com/US/east-palestine-derailment-timeline-key-events-toxic-train/story?id=97522161